
What Is Thread?
As Matter gains traction and establishes itself as the go-to communication standard for connected devices, the term Thread often comes up alongside it. It’s easy to deduce that Thread is some kind of networking protocol, but what exactly is it? How does it differ from other protocols? What are its benefits, and what does it offer that others don’t? And how does Thread relate to Matter?
Thread at a Glance
- Mesh networking protocol
- Low power consumption
- Local communication with low latency
- Simple and streamlined onboarding
- Built-in security by design
- Future-proof and scalable
- Requires a Thread Border Router (such as Homey Pro or Homey Pro mini)
What Is Thread?
Thread is an IPv6-based, low-power wireless networking protocol designed specifically for IoT devices. Built on the same IEEE 802.15.4 radio standard as Zigbee, it forms a secure, scalable mesh network ideal for smart home applications.
Thread was developed by the Thread Group, an alliance of major tech companies including Google, Apple, and Samsung. It was created to address key challenges in traditional IoT protocols, particularly those related to interoperability, security, and reliability.

Thread Is a Mesh Networking Protocol
Like Zigbee and Z-Wave, Thread uses a mesh networking topology, where devices communicate directly with each other and relay messages across the network. This decentralized structure extends coverage, improves reliability, and ensures built-in redundancy and fault tolerance.
In simpler terms, every device in a Thread mesh acts as a node, capable of sending, receiving, and forwarding data. This removes reliance on a single controller and improves the resilience of the entire network.
Thread Device Types and Network Roles
The Thread specification defines two main categories of devices: Full Thread Devices (FTDs) and Minimal Thread Devices (MTDs). Each plays a distinct role within the network.
For a Thread network to operate, it must include at least one Border Router, like Homey Pro or Homey Pro mini. This device acts as a gateway between the Thread mesh and external IPv6 networks (like Wi-Fi or Ethernet), and it also provides internet connectivity to Thread devices.
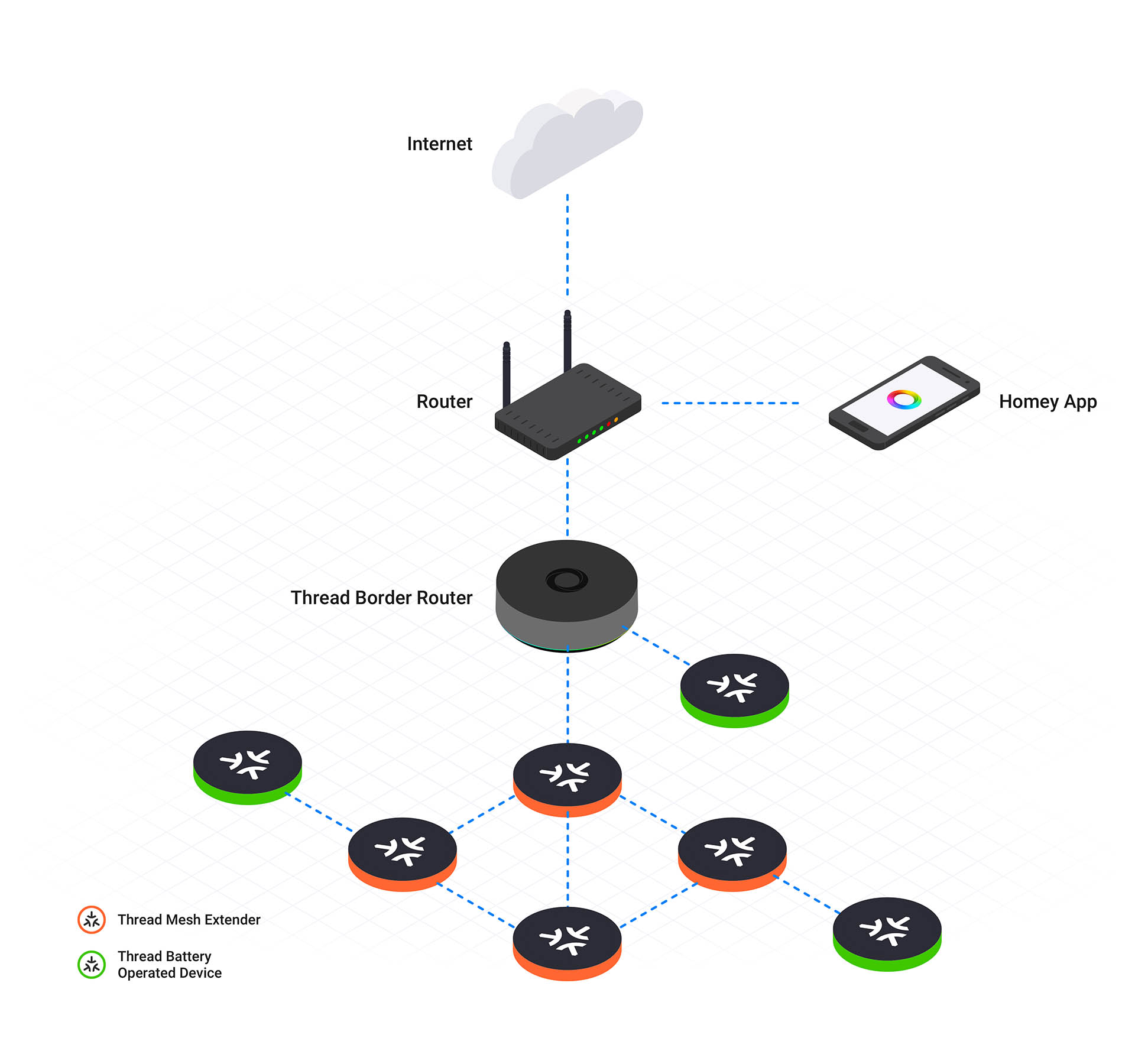
A Thread Router manages routing within the network and handles device security and commissioning. Unlike other devices, routers are always active and do not enter sleep mode. One router is designated as the Leader, responsible for key decisions, such as authorizing devices to become routers. If the Leader becomes unavailable, another router is automatically elected to take its place, ensuring seamless network operation.
FTD and MTD Subtypes
Full Thread Devices (FTDs) and Minimal Thread Devices (MTDs) are further classified as:
- Full Thread Devices (FTD):
- Router-eligible End Device (REED): REEDs have routing capabilities but may not function as routers depending on current network conditions. If needed, the network (via the Leader) can automatically promote a REED to a router without user intervention.
- Full End Device (FED): Similar to REEDs, but without the ability to become a Router or Leader.
- Minimal Thread Devices (MTD):
- Minimal End Device (MED): Communicates only through its parent router and cannot relay messages to other devices. A MED keeps its radio on, even when idle.
- Sleepy End Device (SED): Also relies on its parent router but conserves energy by turning off its radio when idle. It wakes periodically to communicate.
- Synchronized Sleep End Devices (SSEDs): Like an SED, but wakes on a scheduled basis rather than periodically, optimizing communication patterns.
- Bluetooth End Device (BED): Communicates exclusively via a Bluetooth LE Bridge Router and uses Bluetooth Low Energy instead of IEEE 802.15.4. BEDs are distinct from other Thread devices.
If the Thread specification feels overly technical or overwhelming, that’s because it is. The good news is that, as a user, you don’t need to worry about any of these roles. Just set up your Homey Pro or Homey Pro mini and start adding Thread devices. The network takes care of everything else automatically.
Differentiating Between Matter and Thread
Before diving into Thread’s role in the smart home, it’s helpful to understand how it differs from Matter.
- Matter defines the application layer for smart home devices across different manufacturers, ensuring interoperability across ecosystems. It standardizes how devices are set up (like Bluetooth onboarding), how they communicate, what data they exchange, and the security measures they follow.
- Thread, by contrast, is one of the three networking protocols—alongside Wi-Fi and Ethernet—that Matter devices use to talk to each other. It operates at the network layer, providing the underlying infrastructure for fast, secure, and reliable communication between devices.
Let’s break it down with a simple analogy.
Imagine you’re hosting a big party. Matter is like the party planner—it sets the theme, the rules, and makes sure everyone gets along. It ensures that guests from all different backgrounds can mingle, participate, and have a great time. Matter is that friend who effortlessly connects people and keeps the energy high.
Thread, on the other hand, is the layout of the venue—the hallways and pathways that connect everything together. It helps your guests (devices) move from room to room without bumping into walls or getting lost. A well-designed layout makes sure everyone flows smoothly from one part of the party to another.
So while Matter sets the vibe, Thread keeps everything connected. And just like Thread, Wi-Fi and Ethernet are also part of the venue, helping other types of guests get around, always following the planner’s (Matter’s) rules.
Benefits of Thread
Designed specifically for smart devices, Thread offers several key advantages as a mesh networking protocol.
- Low Power Consumption: Thread devices are designed for efficiency, helping to extend battery life for end-devices and reduce power consumption in wired ones.
- Low-Latency Communication: Thanks to efficient routing and low-power radio technology, Thread enables fast, responsive communication with minimal latency.
- Local Connectivity: While a Border Router connects the Thread network to the internet, devices within the network communicate with each other locally. This ensures fast, stable performance without relying on the cloud.
- Resilient and Self-Healing: Thread’s mesh architecture is built for reliability. If one router goes offline, nearby devices automatically re-route through another, keeping the network intact and responsive.
- Strong Security: Thread utilizes built-in encryption and authentication to secure data transmission and safeguard your network against unauthorized access.
- Scalable by Design: Whether you have a handful of devices or hundreds, Thread can scale to meet your needs, making it ready for growing smart homes.
What About Zigbee and Z-Wave?
You may wonder where Zigbee and Z-Wave fit into this, and how they compare to Thread. After all, many of the benefits Thread offers are also found in these established protocols. Let’s break it down.
Both Zigbee and Z-Wave are optimized for low-power devices. However, Thread has a key advantage: it uses the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP), allowing devices to send extremely small messages. This efficiency helps extend the battery life of your smart devices even further.
All three protocols are self-healing, meaning they can reroute data if a node goes offline. But there’s a key difference:
- Zigbee and Z-Wave rely on a central coordinator. If that coordinator fails, the entire network may go down.
- Thread, by contrast, has no single point of failure. If one Border Router fails, another can automatically take over, requiring no user action.
Since Thread is part of the Matter specification, it ensures seamless compatibility across different ecosystems and brands. You don’t have to wonder if device A will work with hub B. It just does.
Thread also takes a stronger stance on security. It mandates features like network-wide encryption, secure onboarding, and support for standard protocols. Z-Wave follows similar security practices, while Zigbee’s security features depend on the specific profile being used.
Finally, consider longevity. Zigbee and Z-Wave are still widely supported, but they are not part of the Matter specification. If you’re just starting out or planning for the future, Thread-enabled devices are your best bet for a smart home that evolves with you.
Homey Pro and Thread
By now, it should be clear that to create a Thread network in your smart home, you need a Thread Border Router. Homey Pro and Homey Pro mini both serve this role. As the world’s most advanced smart home hubs, they support Matter-over-Thread, so any device with the Matter logo will work with Homey Pro right out of the box.
To add a Thread device, you can onboard it using either your Android or iOS device, or directly via the Homey mobile or web app. The latter method is recommended, as it leverages Homey Pro’s built-in Bluetooth radio to pair with your Thread device more easily.
While Thread is currently regarded as the most advanced mesh networking protocol for smart homes, that doesn’t mean you need to limit yourself to it. Homey Pro supports a wide range of technologies, including Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Infrared, and 433 MHz, giving you the flexibility to build a hybrid smart home setup.
Summary
Thread is a mesh networking protocol designed to offer a robust, scalable, and secure foundation for smart home devices. Thanks to its low power consumption, self-healing capabilities, and local communication, it solves many of the limitations found in older wireless protocols, making smart home connectivity more reliable and future-ready.
By creating a Thread network with Homey Pro, you get the best of both worlds: seamless support for Matter-enabled devices and continued compatibility with Zigbee, Z-Wave, and other popular smart home standards.