
What are Heat Pumps and How to Optimize Their Energy Usage in a Smart Home?
Heat pumps are revolutionizing the way we heat and cool our homes. They are a powerful, energy-efficient alternative to traditional HVAC systems like furnaces and air conditioners. Unlike systems that burn fuel or use electricity to create heat, a heat pump simply moves heat from one place to another.
This article explains what residential heat pumps are and how they work. It also shows how integrating them into your smart home can reduce energy use, cut costs, and make your home more comfortable and sustainable.
Contents
- What Are Heat Pumps?
What are heat pumps and what do they do? - The Science Behind a Heat Pump
How do heat pumps work and what components are relevant for energy savings? - Common Types of Residential Heat Pumps
What types of heat pumps are available for homes? - Integrating a Heat Pump into Your Smart Home
How do you connect a heat pump to your smart home? - Optimizing Heat Pump Usage for Energy Savings
How do you use a heat pump intelligently to save money?
What Are Heat Pumps?
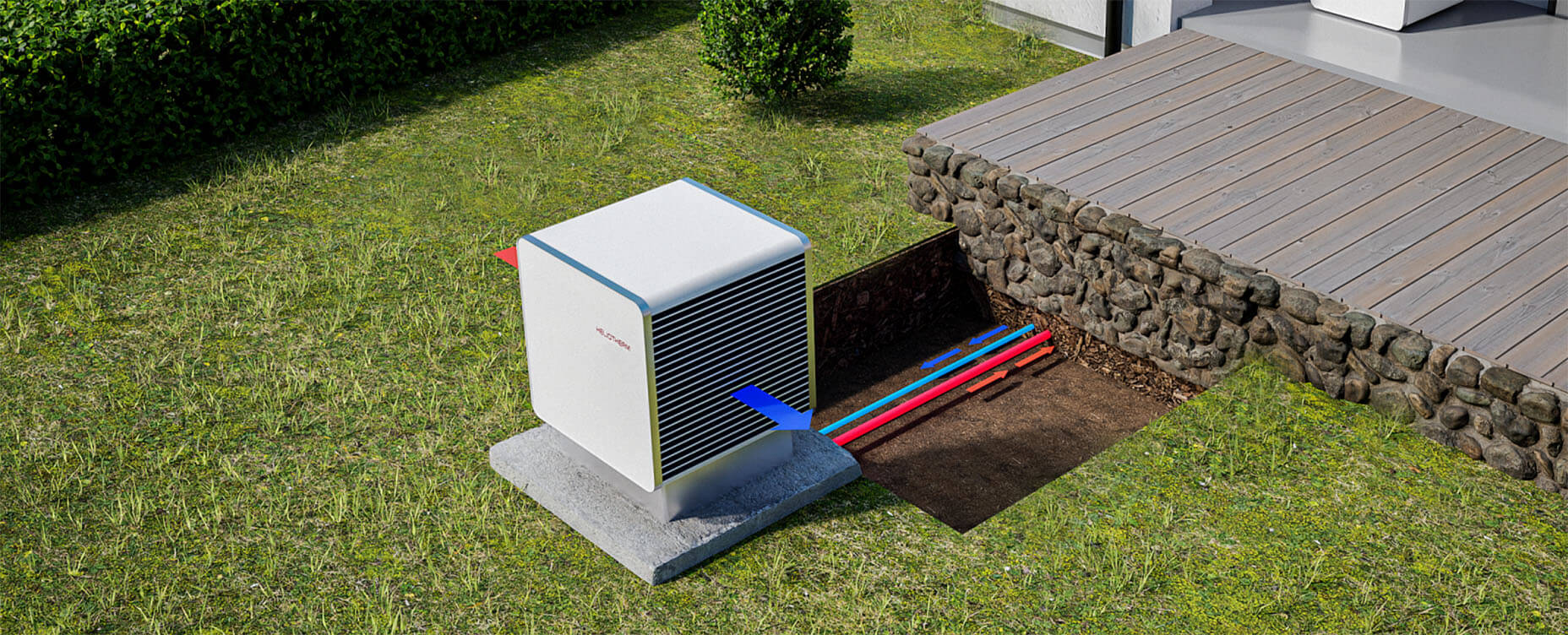
Heat pumps are heating and cooling systems that work by moving heat rather than generating it. In heating mode, they extract warmth from the air, ground, or water outside and transfer it indoors, even when it’s cold outside. In cooling mode, they reverse the process and move heat from inside the home to the outdoors.

Because they move heat instead of creating it, heat pumps are far more energy-efficient than traditional furnaces or boilers. This efficiency translates to lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact, especially when managed via a Home Energy Management System like Homey.
The Science Behind a Heat Pump
A heat pump operates on a fundamental principle of thermodynamics: heat naturally flows from warmer areas to cooler ones. By using a small amount of energy, heat pumps extract heat from a source (outside air, ground, water), and transfer it indoors to warm your home. When you are cooling your home, the flow is reversed and the opposite happens. They extract heat from your home and transfer it outside.
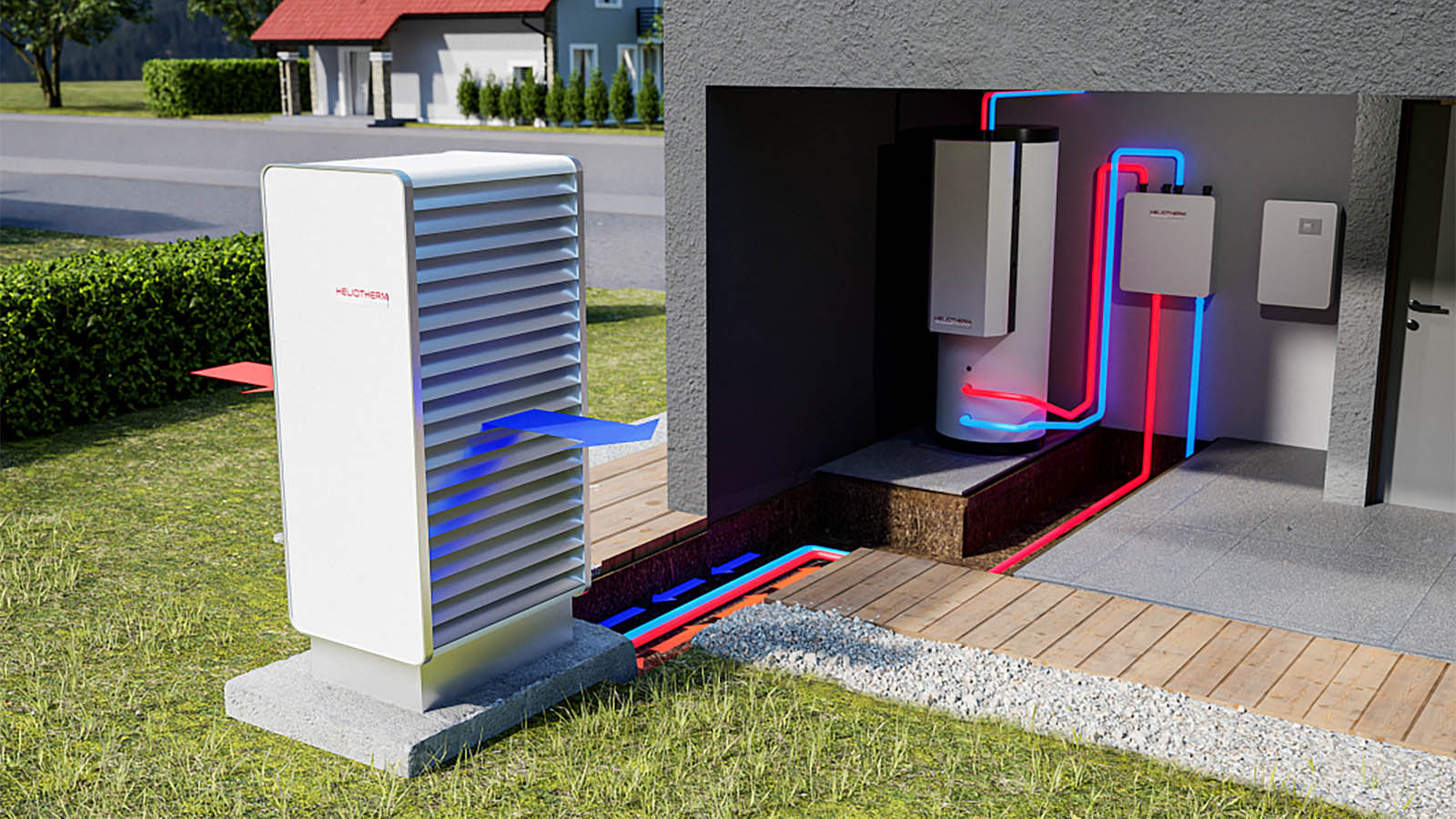
Heat pumps rely on a refrigeration cycle to move heat efficiently between indoors and outdoors. This cycle uses a special fluid called refrigerant, which absorbs heat when it evaporates and releases heat when it condenses. As the refrigerant circulates through the system, it transfers heat from one location to another, heating or cooling your home.
The core components of a heat pump are the compressor, evaporator coil, condenser coil, expansion valve, and reversing valve. The evaporator coil collects heat, the compressor raises the refrigerant’s temperature and pressure, and the condenser coil releases the heat where it is needed. The expansion valve lowers the pressure so the cycle can repeat. Fans push air across the coils, while the reversing valve switches the system between heating and cooling.
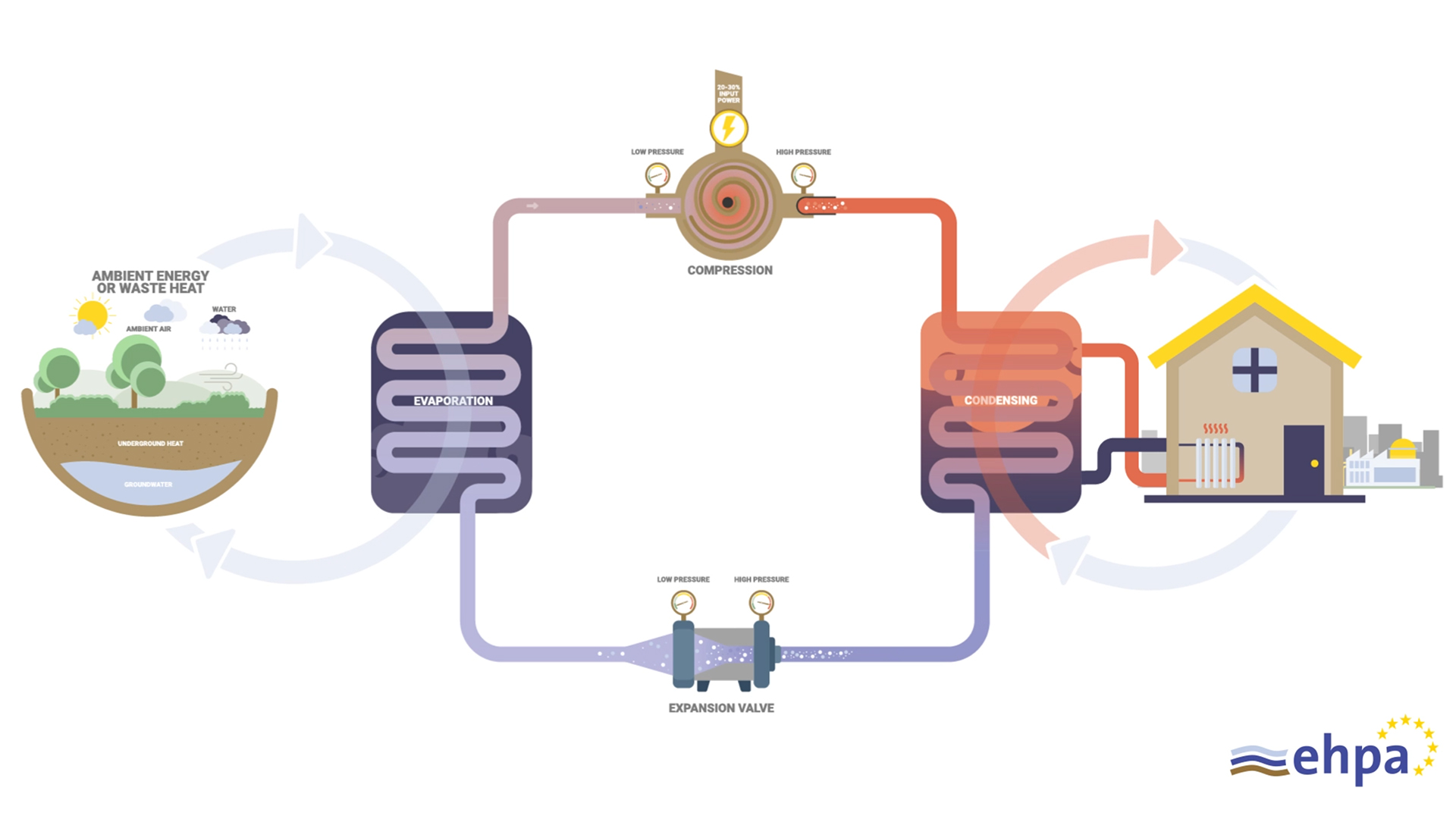
Photo Credit: European Heat Pump Association (EHPA)
Common Types of Residential Heat Pumps
There are several types of heat pumps designed to suit different homes, climates, and installation needs. Each type has its own way of transferring heat and offers unique advantages for efficiency, comfort, and reliability.
Air-Source Heat Pumps
Air-source models are the most common type of residential heat pumps. They work by absorbing heat from the outside air and moving it indoors to heat your home. In warmer weather, they can reverse the process to move heat out of your home, providing cooling. Air-source models are a popular choice because they are typically less expensive and easier to install than other types of heat pumps.
Ground-Source (Geothermal) Heat Pumps
Ground-source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, are highly efficient systems that get their heat from the ground. They use a network of underground pipes to absorb the Earth's stable temperature, which remains consistent all year long. This makes them extremely efficient and consistent, but installation requires digging or drilling, which increases upfront costs. Once installed, they offer low operating costs and can last longer than other systems.
Water-Source Heat Pumps
Water-source heat pumps are similar to ground-source systems but they draw heat from a nearby body of water like a pond, lake, or well. They are highly efficient because water is a very effective conductor of heat. However, they are only a viable option for homes that are located close to a suitable water source.
Hybrid Heat Pumps
Hybrid models typically combine an air-source heat pump with a traditional furnace, automatically switching between the two depending on outdoor temperatures. The heat pump handles the heating needs for most of the year, taking advantage of its high energy efficiency. When temperatures drop below a certain point, the system automatically switches to the furnace, which is more effective in very cold conditions.
Integrating a Heat Pump into Your Smart Home
A heat pump by itself is not inherently smart. The unit’s core components, such as the compressor, coils, and fans, operate on mechanical and electrical controls. What makes a heat pump smart is the addition of a connected controller, usually in the form of a smart thermostat or a manufacturer gateway that links the heat pump to a Home Energy Management System (HEMS) like Homey.
While a smart thermostat offers basic control, such as scheduling and remote access, full smart home integration takes it a step further. Through a platform like Homey, the heat pump can interact with other devices in your home, enabling more advanced automations. For instance, it can work with occupancy sensors to reduce heating when no one is home, adjust cooling based on window or door sensors, or coordinate with solar panels to run when renewable energy is available.
Once your heat pump is paired with a smart home hub like Homey, you can track temperature, humidity, energy usage, or monitor for errors and alarms. You can also set target temperature, create advanced schedules, adjust speed, change operating modes and much more.
If your heat pump is smart grid ready (SG-ready), you unlock some additional benefits.
Learn how to control SG-Ready heat pumps with Homey.
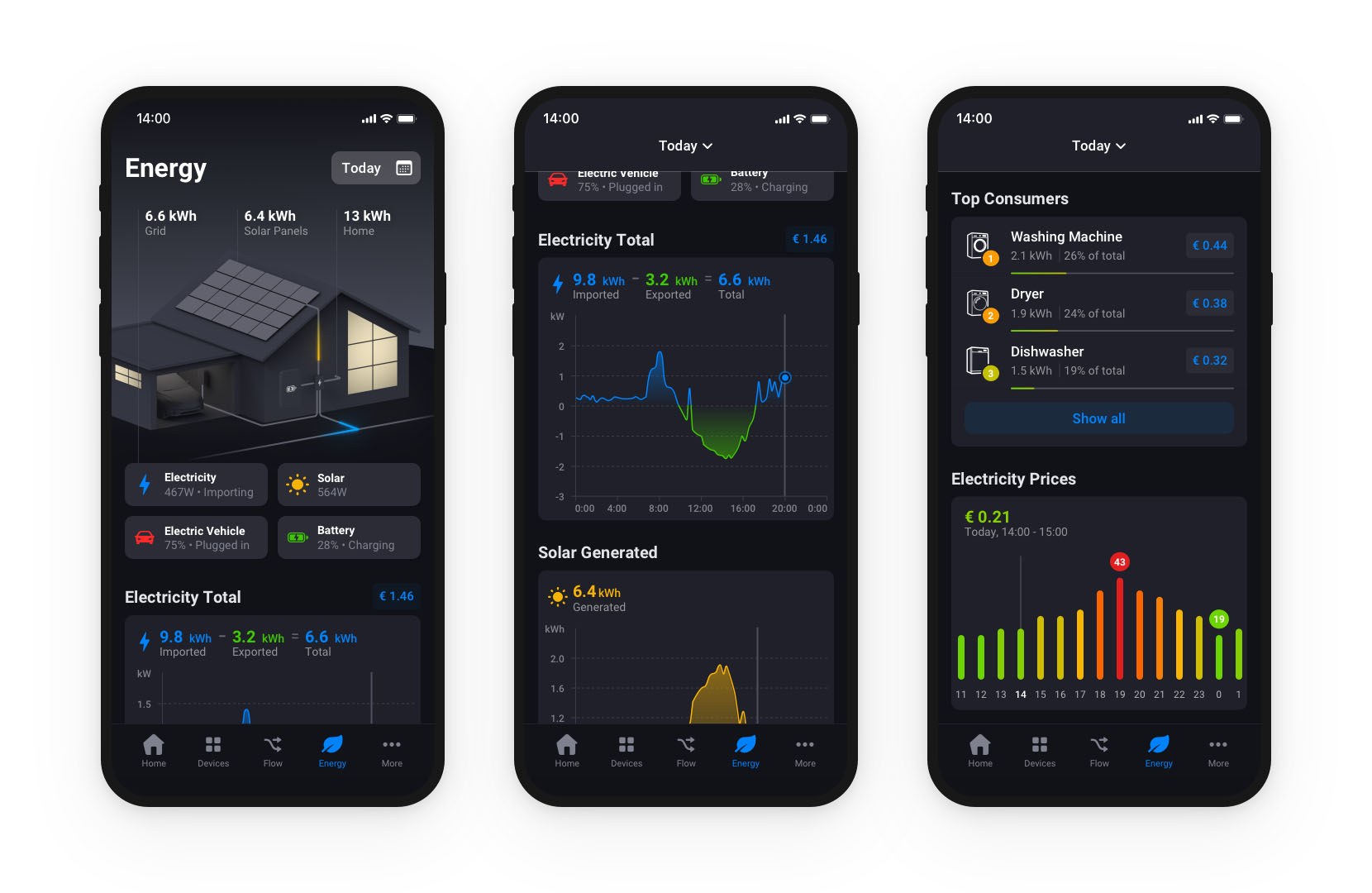
Optimizing Heat Pump Usage for Energy Savings
Integrating a heat pump into a smart home is not only about convenience but also about maximizing efficiency. With the right automations, homeowners can cut energy waste, reduce costs, and get the most out of their system. Here are a few practical ways to optimize heat pump usage for real savings.
Use Off-Peak Electricity Rates
Smart scheduling lets the heat pump run during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper. By pre-heating or pre-cooling your home at those times, it reduces energy costs while maintaining the same level of comfort. Providers like Tibber send real-time pricing data to Homey, allowing the system to automatically shift heat pump operation to the lowest-cost hours without manual intervention.
Combine with Solar Power
Pairing your heat pump with solar panels makes the most of self-generated energy. A smart home system can detect when your panels are producing surplus power and automatically run a heating or cooling cycle. This ensures that renewable energy is used immediately instead of being exported back to the grid at a lower value.
Intelligent Load Balancing
In homes with energy-hungry devices like EV chargers or home batteries, load balancing is essential. A smart system monitors overall consumption and adjusts the heat pump’s usage to prevent overloads and keep everything running smoothly. It can also prioritize critical appliances so that comfort and safety are never compromised.
Weather-Based Scheduling
Weather forecasts allow your smart home to anticipate temperature changes. If a cold front or heatwave is coming, it can start heating or cooling early, easing the heat pump’s workload and improving efficiency. This proactive control keeps indoor temperatures more stable, reduces sudden energy demand spikes, and lowers stress on the system.
Occupancy-Based Control
Connecting the heat pump to smart presence sensors ensures your heat pump only runs when people are home. This prevents wasted energy by lowering output or switching to eco mode when rooms are empty. Homey can also detect when you are approaching your home (traveling home from work) and start your heat pump automatically.

Heating Made Smarter
Heat pumps offer a highly efficient way to heat and cool your home by moving heat rather than generating it. With multiple types available, including air-source, ground-source, water-source, and hybrid, there is a solution for nearly every home, climate, and budget. Pairing a heat pump with smart home technology transforms it into a proactive system that adapts to your lifestyle, comfort needs, and energy availability.
By integrating real-time pricing data, solar production, and weather forecasts, a smart heat pump setup can reduce energy waste, lower utility bills, and extend the life of the system. Platforms like Homey enable advanced automation that makes your home more comfortable, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly, showing that heating and cooling can be both smart and sustainable.






