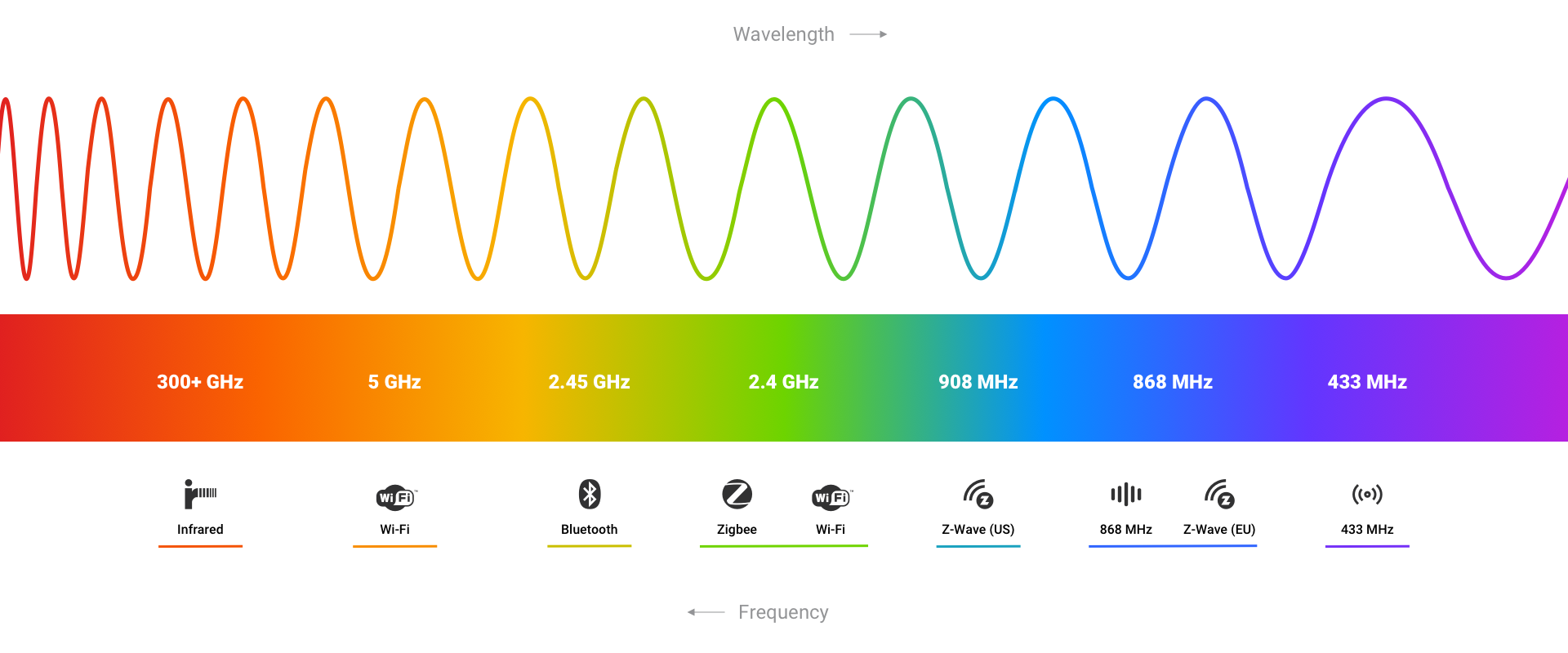
What is 433 MHz?
433 MHz is a term that you might encounter if you’re researching the options for home automation. Companies like Somfy, Nexa, and KlikAanKlikUit offer 433 MHz-compatible devices. So how exactly does this technology work? And what advantages does it provide to your smart home?
433 MHz at a Glance
- Wireless standard used for home control and automation
- Established technology
- Great range, not obstructed by walls
- Budget-friendly
- Easy to set up
- Can serve as an alternative to Zigbee or Z-Wave
- Doesn’t use mesh networking
- Allows only limited communication
- Low power usage & long battery life
- Requires a 433 MHz hub like Homey
Introduction
433 MHz is a wireless radio band on which compatible household devices send signals.
While TVs use infrared light for handling remote control signals, 433 MHz radio waves enable communication with home devices such as motorized blinds from Somfy, KlikAanKlikUit sensors, or socket switches from LightwaveRF.
The technology has been around for a long time, and it’s embedded in plenty of wireless smart home appliances by brands such as Smartwares, Elro, Cleverio, Nexa, or Telldus. Its frequent applications also include key-less entry systems (such as garage or gate openers) and home weather stations.
The technology’s home automation support is why it is one of the seven wireless protocols included in Homey Pro and Homey Bridge.
You might already own a couple of 433 MHz devices, so including them in your smart home system with Homey ensures they don't need to be replaced. In addition, if you ever choose to build a DIY smart home project, the frequency is ideal for amateur radio projects and can make use of your existing equipment. This is possible with the Homey Apps SDK, which Homey developers use to add support for new devices.

433 MHz Pros & Cons
Advantages
Affordable
Implementing 433 MHz in smart home products is quite easy for manufacturers, and that's why these devices tend to be attractively priced.
Long Wireless Range
Compared to infrared, it has one significant advantage when it comes to remote control: it is not blocked by walls, as it’s a radio technology and not a flickering light. For example, when controlling a wall plug hidden behind your sofa or motorized roller blinds in another part of your house, the signal does not get obstructed. For a TV, this is not really necessary, but it makes 433 MHz suitable for home automation purposes.
The overall wireless range is the most significant advantage. The frequency is lower compared to Z-Wave (868-928 MHz), Zigbee (2.4 GHz), or Wi-Fi (2.4 / 5.8 GHz), which makes the point-to-point range of 433 MHz devices impressive. When a 433 MHz hub like Homey sends a command to a device, it can travel over 100 meters (300 feet).
Low Power Consumption
Power usage of 433 MHz devices is also relatively low and comparable to other dedicated home automation standards like Z-Wave or Zigbee. This makes 433MHz also suitable for battery-operated devices like wireless sensors or buttons.
Disadvantages
The technology of 433 MHz brings a number of pros, but it also has considerable downsides you should consider before buying new devices for your smart home.
Not So Smart
The technology itself is rudimentary. Signals are typically only one-way, so a device only sends or receives. The receiver does not confirm commands that are given, so you just have to assume they have been picked up and are being executed. 433 MHz devices, especially sensors, are therefore less reliable than their counterparts functioning on the Zigbee, Z-Wave, Thread and Matter standards.
The devices using this protocol also don’t usually provide information on their battery status or energy consumption. Even though these devices can be battery-powered, there is often no low-battery warning, so you’ll have to keep an eye on them yourself.
No Mesh Networking
433 MHz devices don’t build a mesh network. Mesh networking is a helpful feature that allows devices to relay signals meant for other nodes in the network. It extends the range of your network, as long as other devices are working on the same technology. On top of that, the reliability of your network actually improves when you add more nodes.
Meanwhile, Zigbee and Z-Wave devices do offer this capability, giving them an upper hand.
Transmitter / Receiver Required
433MHz devices cannot communicate directly with your phone or computer, as they don’t feature a dedicated antenna for this technology. This is, however, not different from premium standards like Zigbee and Z-Wave.
What’s in a 433 MHz Connection?
There are three types of devices communicating over the protocol:
- Transmitter
- Receiver
- Transceiver
The transmitter sends information over the 433 MHz radio frequency. The type of information that can be sent is quite limited due to the limited bandwidth, so transmitters usually support only a handful of commands. For instance, a blind remote control might send only requests like up, down, and stop.
The same limitation is in place for the receiver. As a result, your 433 MHz blinds might not even be able to recognize commands like set percentage, but only listen for commands like open or close entirely.
As its name suggests, the transceiver combines the functions of the former two devices, both sending and receiving signals. Homey offers the transceiver capability.
Here’s an example of a setup:
Sophie sets up her smart home using Homey as a smart home hub for her devices. She pairs 2 KlikAanKlikUit Smart Plugs in her bedroom with Homey. After that, the plugs can be turned on or off via the Homey App. Sophie then purchases a Nexa Remote, and she uses two of its buttons to toggle her smart plugs on or off. She also gets a Telldus Motion Sensor, which she can pair with her Zigbee light bulbs and Z-Wave light strips thanks to Homey.

433 MHz & Homey
In order to connect 433 MHz devices directly to your computer or phone, you always need a transceiver or a smart home hub like Homey Pro or Homey Bridge.
With Homey, you don’t have to worry about what RXB6 or Lora antennas do. Homey’s ease of use makes the setup significantly more user-friendly than solutions like Raspberry Pi or Arduino with a dedicated RF transmitter / RF receiver and 433 MHz library.
Additionally, while 433 MHz is a handy technology, its capabilities are quite limited. There’s a wide range of wireless protocols that can power the Smart Home in other ways. We recommend staying versatile with Homey – it includes an antenna covering the European 433 MHz bandwidth, beside also offering Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Infrared connections.

433 MHz Setup Tutorial
Building a 433MHz setup is straightforward. Since it is a wireless technology, there are no wires to install. Because most devices are quite cheap and easy to get, you might even have a set of plugs lying around already.
Step 1: To get started, you only need a smart home hub like Homey Pro or Homey Bridge.
Step 2: Select one or more 433 MHz devices. For instance, a KlikAanKlikUit Bulb and a KlikAanKlikUit Remote Control, and place them where necessary.
Step 3: With the Homey app, you simply open the Devices tab and press the + button. Proceed with the setup based on the device’s instructions. With 433 MHz, it's not necessary to enter passwords or SSIDs like with Wi-Fi. You can typically initiate the pairing process by pressing buttons on the device you want to include in your network and on the controller.
Step 4: Create new Homey Flows with the devices you’ve just set up!
Conclusion
To sum up, 433MHz devices tend to be quite basic. They are priced attractively and have an excellent point-to-point range. A lot of popular brands use 433 MHz as it has been around for a long time and can be added to products fairly easily.
On the other hand, their command set is limited and they don’t give battery warnings. The one-way communication makes 433 MHz devices (primarily sensors) less reliable than those on Zigbee or Z-Wave wireless technologies.
Home automation on 433 MHz is very cost-effective, however, don’t expect the best of the best. For simple socket switches without power measurement or motorized shades and roller blinds, 433Mhz is a good choice.
For lighting, sensors, and security, there are better options. That is why we recommend combining 433MHz automation with another technology like Z-Wave or Zigbee if you want to automate your home completely. Take a look at our summary table:
| Infrared | Wi-Fi | Zigbee | Bluetooth | Z-Wave | 433 MHz | |
| Frequency | 300 GHz | 5 GHz / 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 865 - 926 MHz | 433 MHz |
| Mesh Networking | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Useful Range | 5m | 30m | 15m | 15m | 40m | 100m |
| Power Usage | low | high | low | low | low | low |
| Affordability | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Encryption | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Low Interference | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Hub Not Required | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
In any case, if you don’t want to be restrained by a single smart home communication technology, we highly recommend getting a Homey Pro or Homey Bridge.







